v Context: A report published by United Nations University has warned that 27 of the 31 aquifers in India are depleting faster than they can be replenished.
·
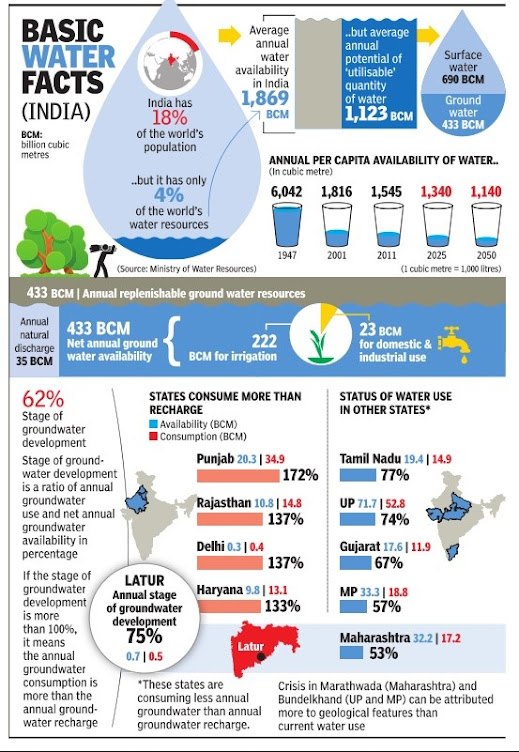
India is the world's largest
groundwater extractor, surpassing China and the US combined.
·
As per the Central Ground Water Board, 70% of India's water
comes from groundwater sources.
Ø
Agricultural overexploitation: Agriculture accounts for over 80% of
groundwater use in India.
Ø
Inadequate regulation: The Mihir Shah Committee highlighted a
lack of focus on institutional innovations in the water sector.
Ø
Climate change: Droughts and rising temperatures
are causing decreased rainfall and increased evaporation, reducing
aquifer recharge.
Ø
Urbanisation: Urbanization creates more impervious surfaces, limiting
groundwater recharge.
Ø
Deforestation: It causes more soil erosion and less
rainfall infiltration.
Ø Subsidies on
electricity and water
Ø
Population growth
Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABY)
·
Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABY) is a central sector scheme of the Ministry
of Jal Shakti.
·
Aim: to improve groundwater
management through community participation.
·
It will be implemented in priority areas across seven states:
Gujarat, Haryana, Karnataka, MP, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, and UP.
·
It is funded by the GoI and the World Bank on a 50:50
basis.
Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch the Rain
·
Catch the
Rain is an annual campaign under Jal Shakti Abhiyan.
·
Aim: to encourage
people to adopt rainwater harvesting practices.
|
ð Jal Shakti Abhiyan was launched in water-stressed
districts by the Ministry of Jal Shakti. ð It focuses on promoting water conservation and water resource
management by:
|
·
NAQUIM is implemented
by the Central Ground Water Board (CGWB).
·
It is a part of the Ground Water Management and Regulation Scheme (a central
sector scheme)
·
Objectives of NAQUIM
are:
v
Delineation & characterisation of aquifers in 3D to
understand their disposition
v
Identification & quantification of groundwater issues
v
Development of groundwater management plans
·
PMKSY is a centrally sponsored
scheme launched in 2015 by the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
· Aims:
v
To enhance physical access to water on the farm
v
To expand cultivable area under assured irrigation
v
To improve on-farm water use efficiency
v
To introduce sustainable water conservation practices
·
The main components of PMKSY are:
- Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme
(AIBP)
- Har Khet Ko Pani (HKKP): It has four sub-components.
1) Command Area
Development (CAD)
2)
Surface Minor Irrigation (SMI)
3)
Repair, Renovation and Restoration (RRR) of Water Bodies
4) Ground Water
Development
- Watershed Development
- Per Drop More Crop
·
The Central and State Governments share funds under the
scheme at a 60:40 ratio, except for the North Eastern and Himalayan
states, where the ratio is 90:10.